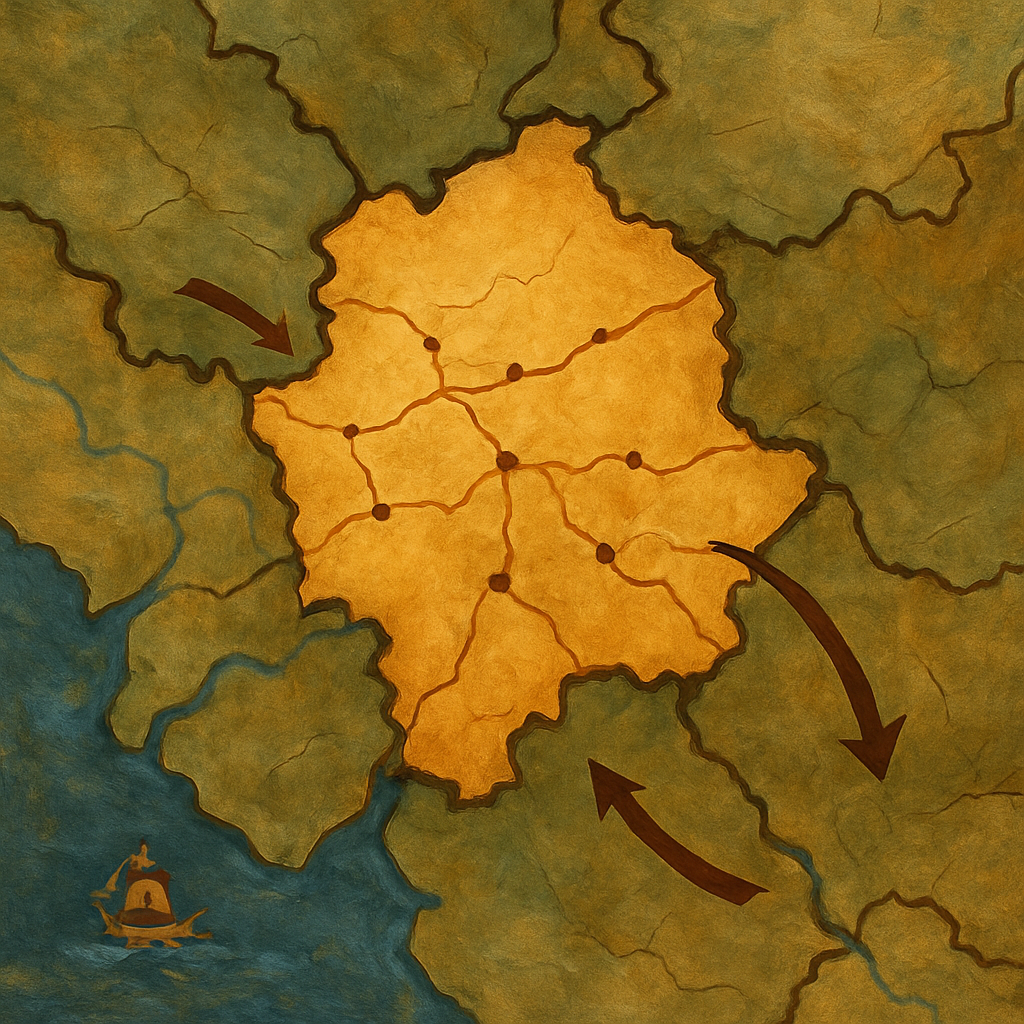
A landlocked country is a nation that lacks a coastline, thus having no direct access to oceanic waters. This geographical limitation impacts a nation’s economic development, trade routes, and international relations significantly. Given maritime trade’s dominance, understanding these impacts is crucial for global economic discussions.
Why Landlocked Status Matters
Landlocked countries face unique economic limitations due to their geography. According to the World Bank, these nations struggle to access international markets efficiently, leading to higher transportation costs and reducing competitive pricing potential domestically.
Key Characteristics of Landlocked Countries
* Geographical Boundaries: Entirely surrounded by other nations.
* Economic Dependencies: Heavy reliance on neighboring countries for seaport access.
* Diplomatic Relationships: Often centered around negotiating transport agreements.
* Limited Direct Trade Routes: Complicated access to global trade networks.
Economic Challenges Faced by Landlocked Nations
Landlocked countries encounter several economic hardships, primarily due to their geographical constraints:
1. Transportation Costs: Without coastal borders, transportation becomes costly and less efficient.
2. Dependency on Neighbors: Countries like Mongolia and Nepal rely on neighbors for shipping access, which makes them susceptible to political disruptions.
3. Economic Growth Barriers: As per the International Monetary Fund (IMF), these countries often show slower economic growth compared to coastal counterparts.
Strategies for Overcoming Economic Challenges
To mitigate economic challenges, landlocked nations are employing innovative strategies:
1. Bilateral Agreements: Developing strong diplomatic ties for seamless access to ports.
2. Infrastructure Development: Investing in robust domestic transport networks (e.g., railways and highways).
3. Economic Diversification: Shifting focus towards industries less reliant on sea access.
Geopolitical Concerns for Landlocked Countries
The absence of a coastline raises significant geopolitical issues:
* Increased Vulnerability: Dependence on surrounding countries can lead to geopolitical tensions.
* Strategic Alliances: To counteract vulnerabilities, landlocked countries often become members of regional organizations, enhancing collective bargaining power.
Environmental Considerations for Landlocked Nations
Environmental issues are prevalent in landlocked regions:
* Water Resource Management: Efficient management is critical in countries like Kazakhstan, where rivers often cross borders.
* Sustainability Practices: Essential to ensure ecological balance, despite external environmental pressures.
Solutions and Success Stories
Examining successful landlocked countries offers valuable insights:
* Switzerland: An economic powerhouse despite being landlocked, thanks to exemplary infrastructure and strong economic policies.
* Rwanda: Leveraging technological innovation and regional partnerships to boost economic growth.
Conclusion: Rethinking Landlocked Status
Understanding the implications of being landlocked is critical for global economic and political strategies. It’s more than a geographical label; it’s about navigating international trade, geopolitics, and environmental management effectively. By exploring successful strategies, these nations showcase resilience and adaptability, altering perceptions and highlighting opportunities within their limitations.
FAQs on Landlocked Nations
What makes a country landlocked?
A landlocked country is completely surrounded by other land masses without any direct access to oceanic bodies.
How do landlocked countries access international trade routes?
They leverage international agreements to gain access through neighboring countries’ transport networks.
Can a landlocked country be economically successful?
Yes, through strategic economic planning, infrastructure development, and diversification of industries, many landlocked countries thrive economically.
Are all landlocked countries economically disadvantaged?
Not necessarily; while challenges exist, strategic policies and regional cooperation can significantly mitigate impacts.
References
* World Bank Reports on Economic Challenges of Landlocked Countries.
* International Monetary Fund (IMF) Economic Analyses.
* Case Studies on Switzerland’s and Rwanda’s Economic Strategies.