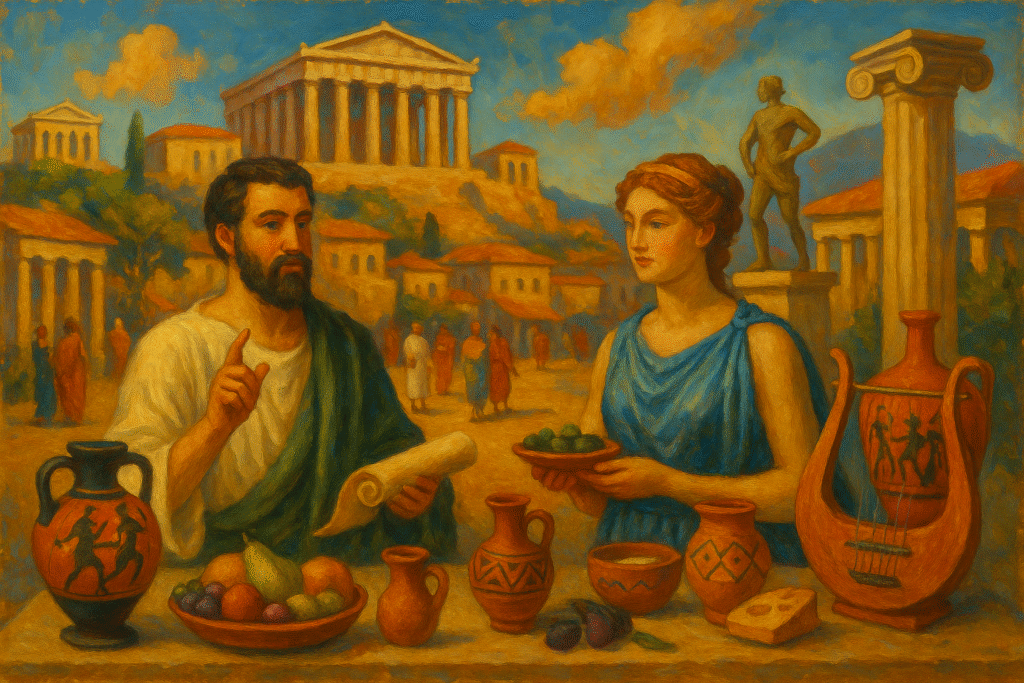
The civilization of ancient Greece stands as a beacon of cultural and intellectual achievement, captivating minds for centuries. Its allure lies in the remarkable contributions it has made to modern society, shaping arts, governance, philosophy, and more. By understanding this illustrious past, we can appreciate how deeply its roots intertwine with our world today, from democratic ideals to the foundations of Western philosophy.
Ancient Greek Food: Daily Diet and Culinary Traditions
Central to daily life, the ancient Greek diet emphasized simplicity and sustainability, driven by its agrarian society. Staples such as wheat and barley formed the basis of their diet, often prepared into bread. Olive oil, another cornerstone, not only flavored foods but also served significant economic and religious roles. Cheese, wine, and honey were revered additions that embellished their meals, reflecting a resourceful use of available produce.
Communal meals held immense social importance, fostering bonds within families and communities. A traditional _symposium_, for instance, celebrated intellectual exchange over shared meals, embedding a sense of camaraderie and cultural continuity. Agriculture, deeply intertwined with these practices, sustained the population through the cultivation of essential crops like grapes, olives, and various grains. This harmonious balance of sustenance and celebration remains a defining feature of ancient Greek culture.
Education in Ancient Greece: Shaping Young Minds
Education in ancient Greece was a product of its diverse city-states, with Athens and Sparta embodying contrasting educational philosophies. In Athens, the focus was on fostering a well-rounded education that embraced arts, sciences, and physical training, shaping citizens skilled in rhetoric and philosophy. This contrasted with Spartan education, which prioritized discipline and military prowess over intellectual pursuits.
Tutors played a pivotal role in Athenian education, guiding youths in rhetoric and philosophy — essential skills for future leaders. Philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle left indelible marks on educational thought, emphasizing logic, ethics, and the pursuit of wisdom. Their teachings paved the way for educational systems that value critical thinking and holistic development, principles that resonate within modern educational philosophies.
Gender Roles in Ancient Greece: Men and Women in Society
Ancient Greek society was largely patriarchal, with distinct roles and duties for men and women. Men were often engaged in public life, responsible for political decisions and community governance. Women’s roles were predominantly domestic, managing households and raising children, though this did not preclude all public engagement.
Despite societal constraints, figures like Sappho and Aspasia emerged as influential women breaking traditional molds. Sappho’s poetic prowess celebrated the complexities of human emotions, while Aspasia’s intellectual contributions influenced prominent thinkers, attesting to the undercurrents of female empowerment within a male-dominated society.
Ancient Greek City-States: Urban Planning and Governance
The city-states, or _polis_, of ancient Greece, such as Athens and Sparta, featured unique urban planning and governance systems. Key public areas like the Agora and Acropolis facilitated civic engagement, commerce, and religious activities, creating hubs of economic and spiritual life.
Private residences juxtaposed these public spaces, reflecting a clear divide yet complementing the synergy of daily interactions. Governance varied among city-states, blending oligarchic, democratic, and militaristic systems, influencing administrative structures worldwide. These city-states laid the groundwork for modern governance, emphasizing civic participation and localized administrative authority.
Daily Routines: A Snapshot of Life in Ancient Greece
A typical day in ancient Greece began with morning rituals that blended spiritual devotion and practical tasks. Citizens engaged in various occupations, from agriculture to craftsmanship, reflecting a society deeply connected to its environment.
Leisure periods featured cultural activities such as theatre, athletic contests, and music, embodying the Greek appreciation for beauty and excellence. Festivals, vibrant with communal spirit, punctuated the year, honoring deities and marking seasonal changes, underscoring the vital link between religious observance and social life.
Crafting Art and Culture: The Creative Spirit of Ancient Greece
Myth and legend permeated every layer of ancient Greek daily life, offering a rich tapestry of stories that influenced cultural practices. Artistic pursuits flourished, evident in the era’s exquisite sculpture, pottery, and theatre, encapsulating the values and ideals of the time.
These cultural expressions established social norms and collective identity, with mythology shaping perceptions of heroism, morality, and human endurance. Ancient Greek art, in its varied forms, remains a testament to their pursuit of perfection, both in beauty and thought.
Legacy of Ancient Greece: What We Can Learn Today
The legacy of ancient Greece extends beyond history books, influencing contemporary educational and social systems. The philosophical ideals championed by Greek thinkers encouraged rationality and ethics, cornerstones of modern governance and personal development.
Greek cuisine, arts, and cultural traditions continue to inspire and infuse our world, reminding us of the enduring power of a civilization that cherished beauty, wisdom, and community.
FAQs About Daily Life in Ancient Greece
* What did ancient Greeks eat on a daily basis?
Ancient Greeks primarily consumed a diet of bread, olives, cheese, and wine, supplemented by fruits, vegetables, and occasional meats.
* How were children educated in ancient Greece?
Athenian education emphasized a balanced curriculum of arts and sciences, while Sparta focused on military training.
* What were the roles of men and women in this society?
Men participated in politics and commerce, while women managed households, though some, like Sappho, achieved cultural prominence.
* How were Greek cities organized and governed?
Greek city-states featured public spaces like the Agora for civic activities, with governance systems that ranged from democracies to oligarchies.
* What cultural practices were unique to ancient Greece?
Practices such as symposiums, theatre, and the Olympic Games are cultural hallmarks that originated in ancient Greece.
For further insights into ancient Greek civilization and its influence, delve deeper into specific aspects and explore how these timeless contributions continue to shape our lives today.